Accounting glossary - dictionary_6
Thông tin tài liệu:
Nội dung trích xuất từ tài liệu:
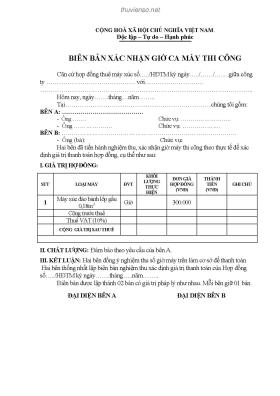
Accounting glossary - dictionary_6http://www.ventureline.com/glossary.aspbusiness loans. Rates in general tend to rise with inflation and in response to theFederal Reserve raising key short-term rates. A rise in interest rates has anegative effect on the stock market because investors can get more competitivereturns from buying newly issued bonds instead of stocks. It also hurts thesecondary market for bonds because rates look less attractive compared tonewer issues.INTERFUND LOAN is an authorized (usually) short term loan from one fund toanother.INTERIM AUDIT is an audit conducted during the fiscal year usually as a meansof minimizing the work and time involved in concluding the audit after the fiscalyear. A corporation might have an interim audit covering the first nine months ofthe fiscal year so that at the end of the fiscal year most of the auditing will focuson the last three months of the fiscal year thus allowing for a comprehensiveaudit and early completion of the audit reports. An interim audit does not usuallyyield any formal reports from the external auditors.INTERIM DIVIDEND is the declaration and payment of a dividend prior to annualearnings determination.INTERIM EARNINGS see INTERIM STATEMENT.INTERIM STATEMENT is a financial report covering only a portion of a fiscalyear (prepared by accountants, but usually unaudited). Quarterly statementsfrom publicly traded companies are one example of an interim statement. Interimstatements are not as detailed or as exact as annual statements.INTERMEDIARY is the person or institution empowered to be the intermediary inmaking investment decisions for others. Examples: banks, savings and loaninstitutions, insurance companies, brokerage firms, mutual funds, and creditunions.INTERMEDIATION COST, in finance, is the cost involved in the placement ofmoney with a financial intermediary. The person or institution empowered as theintermediary to make investment decisions for others. Examples: banks, savingsand loan institutions, insurance companies, brokerage firms, mutual funds, andcredit unions.INTERNAL AUDIT is an independent appraisal function established within anorganization to examine and evaluate its activities as a service to theorganization. The objective of internal auditing is to assist members of theorganization in the effective discharge of their responsibilities. To this end,internal auditing furnishes them with analyses, appraisals, recommendations,counsel, and information concerning the activities reviewed. The audit objectiveincludes promoting effective control at reasonable cost. Occasionally a 101http://www.ventureline.com/glossary.aspcorporation may contract an external auditor or firm to conduct its internal auditfunction.INTERNAL AUDITOR is an auditor who works directly for a company auditing itsactivities throughout the year. Internal auditors of corporations are often notcertified auditors, though they usually have significant accounting experience.They should report directly to the board of directors of the corporation.INTERNAL CONTROLS include policies and procedures that (a) pertain to themaintenance of accurate and reasonably detailed records, (b) providereasonable assurance that transactions are properly recorded and authorized,and (c) safeguard assets.INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR) is also called the dollar-weighted rate ofreturn; the interest rate that makes the present value of the cash flows from allthe sub-periods in an evaluation period plus the terminal market value of theportfolio equal to the initial market value of the portfolio.INTERSEGMENT REVENUE is revenue generated within a segment; whether itbe a business or geographical segment.IN THE BLACK means making money; the opposite of in the red.IN THE RED means losing money; the opposite of in the black.INTRACOMPANY means occurring within or taking place between branches oremployees of a company.INTRINSIC VALUE, generally, is the value of a resource unto itself, regardless ofits value to humans; often considered the ethical value of a resource, or the rightof the resource to exist, e.g., in securities, it is the perceived actual value of asecurity, as opposed to its market price or book value.INVENTORY for companies: includes raw materials, items available for sale or inthe process of being made ready for sale (work in process); for securities: it issecurities bought and held by a broker or dealer for resale.INVENTORY LOAN is loan that is extended based upon the, usually, discounted/ factored value of a business inventory.INVENTORY OBSOLESCENCE is when inventory is no longer salable. Possiblydue to too much inventory on hand, out of fashion or demand. The true value ofthe inventory is seldom exactly what is shown on the balance sheet. Often, thereis unrecognized obsolescence. 102http://www.ventureline.com/glossary.aspINVENTORY SHRINK, as used in retail, is reduction in physical inventory causedprimarily by shoplifting and employee theft.INVENTORY SHRINKAGE is a reduction in the physical amount of inventory thatis not easily explainable. The most common cause of shrinkage is theft.INVENTORY TURNOVER is a ratio that shows how many times the inventory ofa firm is sold and replaced over a specific period.INVENTORY TURNS (Period Average) measures the average efficiency of thefirm in managing and selling inventories during the last period, i.e., how manyinventory turns the company has per period and whether that is getting better orworse. It is imperative to compare a company’s inventory turns to the industryaverage. A company turning their inventory much slower than the industryaverage might be an indication that there is excessive old inventory ...
Tìm kiếm theo từ khóa liên quan:
tài liệu tài chính tài liệu kế toán kiểm toán đầu tư tài chính kiến thức tài chính thị trường tài chínhTài liệu có liên quan:
-
Giáo trình Thị trường chứng khoán: Phần 1 - PGS.TS. Bùi Kim Yến, TS. Thân Thị Thu Thủy
281 trang 1022 34 0 -
2 trang 527 13 0
-
18 trang 465 0 0
-
2 trang 365 13 0
-
293 trang 335 0 0
-
Giáo trình Đầu tư tài chính: Phần 1 - TS. Võ Thị Thúy Anh
208 trang 296 8 0 -
Nghiên cứu tâm lý học hành vi đưa ra quyết định và thị trường: Phần 2
236 trang 236 0 0 -
Nhiều công ty chứng khoán ngược dòng suy thoái
6 trang 213 0 0 -
Ứng dụng mô hình ARIMA-GARCH để dự báo chỉ số VN-INDEX
9 trang 164 1 0 -
Bài giảng Đầu tư tài chính - Chương 6: Phân tích công ty và định giá chứng khoán
11 trang 142 0 0 -
Blockchain – khởi nguồn của một nền kinh tế mới: lời mở đầu
93 trang 132 0 0 -
88 trang 132 1 0
-
Bài giảng Đầu tư tài chính - Chương 1: Tổng quan về đầu tư tài chính
25 trang 123 2 0 -
Ebook 9 quy tắc đầu tư tiền bạc để trở thành triệu: Phần 1
125 trang 120 0 0 -
Giáo trình Đầu tư tài chính: Phần 2 - TS. Võ Thị Thúy Anh
205 trang 116 6 0 -
Ngân hàng câu hỏi trắc nghiệm về tài chính ( kèm đáp án)
16 trang 111 0 0 -
2 trang 105 0 0
-
Giáo trình Tài chính tín dụng: Phần 1 - ThS. Huỳnh Kim Thảo
29 trang 104 0 0 -
Thị trường bảo hiểm Việt Nam: sự phát triển, cơ hội và thách thức
8 trang 100 0 0 -
Tiểu luận: Phân tích báo cáo tài chính NH TMCP Techcombank giai đoạn 2008 - 2012
34 trang 97 0 0